Sintered Stainless Steel “Fiber” Filters - Details
|
|
|
T.S.Absolute ®
|
Comparison of Stainless Steel Filters: Sintered Powder vs Sintered Fiber
Generally filters play an important role in versatile fields of fluidic filtration.
Specifically, in liquid chromatography, filters are indispensable, improving
the service life and stability of the analyzer and systems, and affecting
the analysis data.
Filters in HPLC systems, for example, will be used to remove micro particles
contained in solvents, discharged out of pumps, mixed in samples and pushed
out of columns.
Filters in column plugs will also prevent packing materials from running
out of columns.
|
|
Drawbacks of Conventional Filters:
The most commonly used filters at present are sintered stainless steel powder filters which, however, cannot comply with the increasing demands in micro HPLC applications for higher filtration capability with minimized volume and dimensions.
Shown below is the microscopic photo of a sintered 10 µm diameter
powder filter to be used as a solvent filter, proving a wide deviation
in powder diameter from some ten micro meters through one hundred and some
tens micro meter and uneven distribution of pore size.
With the lower void rate shown in the photo, fluid resistance will increase greatly, as the filter pore size get smaller.
|
The sintered powder filters consisting of powder particles connected with
one another at contact points will be easily broken if the thickness of
the filters has to be reduced.
The filters will need one through two mm thickness minimum.
|
 |
|
Drawbacks:
1)Owing to the restriction in minimum thickness available, the filter volume cannot be reduced to such a level as to fulfill the requirements in micro HPLC applications.
2)The filters with lower void rate will be clogged in a shorter time, when the pore sizes get smaller.
3)The volume of the filters made of powder cannot be diminished drastically. The pore size cannot be smaller than one through two µm.
Sintered Stainless Steel Fiber Filters in Paper Form:
The sintered fiber filters in paper form will comply with the requirements
which the sintered powder filters cannot realize (See the microscopic photo
lower right).
The filters with surface treatment will provide an efficient filtration,
even with the pore size of 0.2 µm or smaller.
|
 |
Advantages of Sintered Fiber Filters:
1)Micro pore with ultra fine fiber of 1 µm diameter.
2)Uniform pore size with uniform fiber diameter.
3)Higher physical strength with fibers connected at multi points.
4)Higher flexibility. Possible to be bent. |
| Fiber diameters |
1, 2, 4, 8, 12µm |
| Filter thickness |
50 - 400µm |
|
|
Comparison of Filter Capability in GPC:
Performance of in-line filters at column and detector:
With a light scattering detector and an RI detector
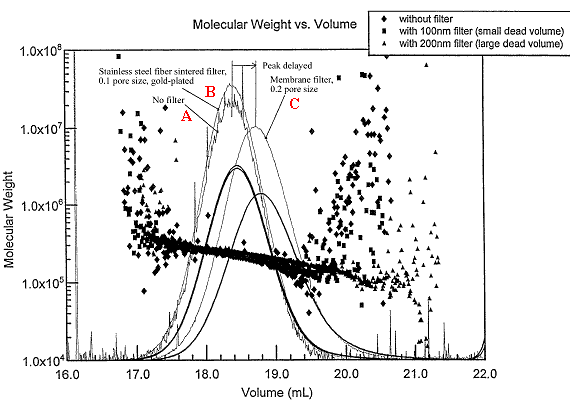 |
A: No filter
B: Gold-plated TS Absolute filter, pore size of 0.1µm
C: Conventional membrane filter, pore size 0.2µm |
Noise reduced with the sintered stainless steel fiber filter or the conventional membrane filter. But the peak got broad and changed the position when the conventional membrane filter was applied.
With the sintered stainless steel fiber filter TS Absolute, however, the peak stayed at the same position with the same shape thanks to the minimized inner volume of the filter.
Since the peak position and the constant shape are critical in GPC, the
conventional membrane filter will be less suitable than TS Absolute filter
for the precise particle filtration to eliminate detector base line noise.
|
Filter Surface Treatment:
Gold, silver plating or PTFE coating are available on the filter with fibers connected at multi points and with uniform pore size. Reduction on pore size and improvement on filtration efficiency are realized.
Examples of applications:
< Gold or silver plating >
Ultra micro particle filtration (0.1 µm particles will be caught
with the gold plated filter)
< PTFE coating >
High efficiency in water filtration. Chemically inert filtration.
|
|
|
|
|